Turkish Air Forces F-104 G (32001) Tigermeeters
Turkey is one of the very first countries to receive the F-104Gs within the MAP program. As a preparation for the new aircraft the 144th Squadron was organised at the 4th AB in Mürted-Ankara. The first 15 aircraft arrived on May 10th,1963 by sea and they were deployed at the newly founded squadron in July. In July 1963 two TF-104gs arrived and they were also assigned to the same squadron. This was followed by Canadair produced 18 F-104Gs and 2 TF-104Gs. The shipment continued in 1965 with 5 more Canadair built F-104Gs. All of these planes were deployed at the 144th Squadron. In 1968 3 pcs F-104G and 1 pc TF-104G were received from USAF.
The TuAF faced with the US embargo after the Cyprus peace-keeping Operation ordered a batch of 18 F-104S from Italy. 6 of the planes were delivered within the same year and the remainder in 1975 on the basis of the planes per month. In 1975 the purchase was risen to 40 planes all which were received within 1976.
The CF-104s, F-104Gs, TF-104Gs and the RF-104Gs which were strated being replaced by more modern aircraft were despatched to Turkey. This operation included 17 pcs F-104Gs from Belgium, 43 pcs F-104Gs & 12 pcs TF-104Gs from Holland, 12 pcs RF-104G and one TF-104G from Norway and 165 pcs F-104Gs and 36 pcs TF-104Gs from Germany. Canada also promised to hand over the CF-104s after being replaced by the F-18A/Bs. In 1986 44 pcs CF-104G & 6 pcs CF-104D were received. These planes were allocated to the 181st and to the 182nd Squadrons.

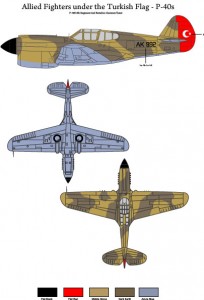
Turkish Air Forces P-40E and P-40B(72001)
This decal set corresponds to the markings on the P-40B and P-40E aircrafts that served in the Turkish Air Force in the period of 1942-1948. The set allows you to complete 3 full profiles. This top quality decal set is printed by the company Microscale.
It is possible to make 2 full profiles of the E model with 6 different number alternatives. The guidebook enclosed to the sticker set demonstrates in details painting patterns and marking emplacements.





Turkish Air Forces P-47D Thunderbolt Stars and Crescent with Nose Arts(72002)
Among the most famous aircrafts of World War Two, P-47D Thunderbolts were used in the Turkish Air Force in the period of 1947-1954. Used at first in the 9th, 5th and 8th air regiments, the total number of aircrafts that came was 180.
Our decal set is made for use on models scaled 72 and 48 and comprises decals to complete a total of three aircraft models.


F-102A Delta Dagger Case X(72003)


P-47 in Foreign Air Forces Around the World (72004)
Among the most famous aircrafts of World War Two, P-47D Thunderbolts were used in the Turkish, Iranian and Yugoslav Air Forces in the period of 1945-1962.
Our decal set is made for use on models scaled 48 and comprises decals to complete a total of three aircraft models.

Spitfires and Wurgers of the Turkish Air Force (72005)




Mediterranean C-47’s (72006)
110 C-47A/Bs and DC-3s served the Turkish Armed Forces and the Turkish Air Force. But it was the Turkish State Airlines who was the first to buy 30 C-47s from the RAFME stocks in Cairo in 1945 in order to renew the fleet and to expand the existing routes. This was followed by the procurement of 18 C-47As with the sources allocated from the national budget in 1946. They joined The Turkish Armed Forces in 1948. It was soon followed by 81 C-47A/Bs supplied from the USAF stocks in Germany within the American Military Aid Programme, The shipment started in August 13, 1948 and it was completed in April 24, 1949. But 7 of these planes which arrived in 1949 were then delivered to an unknown destination most probably to Persia within the same year(1). The last C-47s added to the inventory were 11 planes 2 of which were acquired from Libya, one from the Turkish Airport Authorithies (DHMI) and one from the Turkish Mineral Exploration Agency (MTA) one from USAFE and 6 from THY (Turkish Airlines) which were used as VIP transports. The planes which were acquired from USAFE and THY were given the Turkish Military Serials which were previously assigned to those 7 planes delivered to an unknown destination(1).
C-47s served in the TuAF for a long period of time and they often worked side by side with C-130s and with C-160s. They flew the “Western Courier” and the “Eastern Courier” routines starting from the Etimesgut Military Airport. They were started to be replaced by the CASA CN-235s in Dec. 1993. Three EC-47s which were converted into ECM planes remained in service until 1995. The last C-47 was replaced in 1998.


Turkish Spitfires (72007)

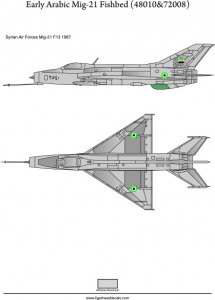
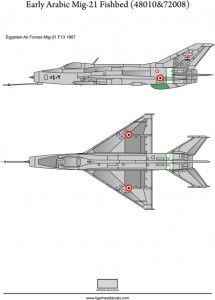
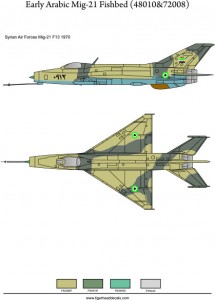
Early Arabic Mig-21 F13 Fishbeds(72008)
The Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-21 (Russian: Микоян и Гуревич МиГ-21; NATO reporting name: Fishbed) is a supersonic jet fighter aircraft, designed by the Mikoyan-Gurevich Design Bureau in the Soviet Union. It was popularly nicknamed “Balalaika”, from the aircraft’s planform-view resemblance to the Russian stringed musical instrument or ołówek (English: pencil) by Polish pilots due to the shape of its fuselage.
Early versions are considered second-generation jet fighters, while later versions are considered to be third-generation jet fighters. Some 50 countries over four continents have flown the MiG-21, and it still serves many nations a half-century after its maiden flight. The fighter made aviation records. At least by name, it is the most-produced supersonic jet aircraft in aviation history and the most-produced combat aircraft since the Korean War, and it had the longest production run of a combat aircraft (1959 to 1985 over all variants)


Turkish Air Forces TF-104 G (72009) Tigermeeters
Turkey is one of the very first countries to receive the F-104Gs within the MAP program. As a preparation for the new aircraft the 144th Squadron was organised at the 4th AB in Mürted-Ankara. The first 15 aircraft arrived on May 10th,1963 by sea and they were deployed at the newly founded squadron in July. In July 1963 two TF-104gs arrived and they were also assigned to the same squadron. This was followed by Canadair produced 18 F-104Gs and 2 TF-104Gs. The shipment continued in 1965 with 5 more Canadair built F-104Gs. All of these planes were deployed at the 144th Squadron. In 1968 3 pcs F-104G and 1 pc TF-104G were received from USAF.
The TuAF faced with the US embargo after the Cyprus peace-keeping Operation ordered a batch of 18 F-104S from Italy. 6 of the planes were delivered within the same year and the remainder in 1975 on the basis of the planes per month. In 1975 the purchase was risen to 40 planes all which were received within 1976.
The CF-104s, F-104Gs, TF-104Gs and the RF-104Gs which were strated being replaced by more modern aircraft were despatched to Turkey. This operation included 17 pcs F-104Gs from Belgium, 43 pcs F-104Gs & 12 pcs TF-104Gs from Holland, 12 pcs RF-104G and one TF-104G from Norway and 165 pcs F-104Gs and 36 pcs TF-104Gs from Germany. Canada also promised to hand over the CF-104s after being replaced by the F-18A/Bs. In 1986 44 pcs CF-104G & 6 pcs CF-104D were received. These planes were allocated to the 181st and to the 182nd Squadrons.

Turkish Air Forces F-104 G (72010) Tigermeeters

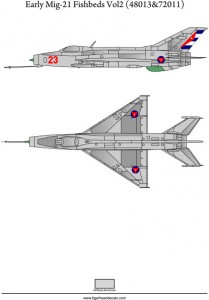
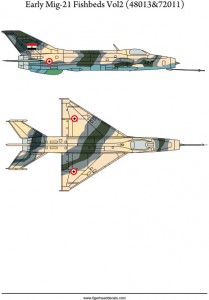
Early Mig-21 Fishbeds Volume 2 (72011)
The Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-21 (Russian: Микоян и Гуревич МиГ-21; NATO reporting name: Fishbed) is a supersonic jet fighter aircraft, designed by the Mikoyan-Gurevich Design Bureau in the Soviet Union. It was popularly nicknamed “Balalaika”, from the aircraft’s planform-view resemblance to the Russian stringed musical instrument or ołówek (English: pencil) by Polish pilots due to the shape of its fuselage.
Early versions are considered second-generation jet fighters, while later versions are considered to be third-generation jet fighters. Some 50 countries over four continents have flown the MiG-21, and it still serves many nations a half-century after its maiden flight. The fighter made aviation records. At least by name, it is the most-produced supersonic jet aircraft in aviation history and the most-produced combat aircraft since the Korean War, and it had the longest production run of a combat aircraft (1959 to 1985 over all variants)




Hawker Sea Fury (72012)(SOLD OUT!!!)
The Hawker Sea Fury was a British fighter aircraft designed and manufactured by Hawker. It was the last propeller-driven fighter to serve with the Royal Navy, and also one of the fastest production single piston-engined aircraft ever built. Developed during the Second World War, the Sea Fury entered service two years after the war ended. The Sea Fury proved to be a popular aircraft with a number of overseas militaries, and was used during the Korean War in the early 1950s.
The Sea Fury’s development was formally initiated in 1943 in response to a wartime requirement of the RAF, thus the aircraft was initially named Fury. As the Second World War drew to a close, the RAF cancelled their order for the aircraft; however, the Royal Navy saw the type as a suitable carrier aircraft to replace a range of increasingly obsolete or poorly suited aircraft being operated by the Fleet Air Arm. Development of the Sea Fury proceeded, and the type began entering operational service in 1947.



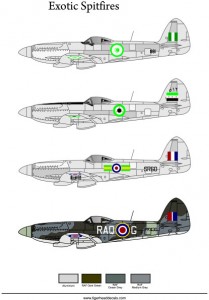
Exotic Spitfires (72013)
The Rolls-Royce Griffon engine was designed in answer to Royal Naval specifications for an engine capable of generating good power at low altitudes. The concepts for adapting the Spitfire to take the new engine had begun as far back as October 1939; Joseph Smith felt that “The good big ‘un will eventually beat the good little ‘un.” and Ernest Hives of Rolls-Royce thought that the Griffon would be “a second power string for the Spitfire.”[1] The first of the Griffon-engined Spitfires flew on 27 November 1941.
Although the Griffon-engined Spitfires were never produced in the large numbers of the Merlin-engined variants they were an important part of the Spitfire family and, in their later versions, kept the Spitfire at the forefront of piston-engined fighter development.
It is possible to make 4 full profiles.
– Royal Air Force
– Southern Rhodesia Air Force
– Egyptian Air Force
– Syrian Air Force.

Hellenic Spitfires (72014)
The 336th Sqdn “Olympus” received the first Spitfire. The receival of new Spits took place at Araxos AB on 14-11-1944. In the end of 1945 RHAF stopped being depended on RAF and the mk.Vb/c were given to Greece on 25/4/1946. In January 1947 were delivered the Spitfires mk.IX. On the February of 1949, were delivered the new Spitfires mk.XVIe.



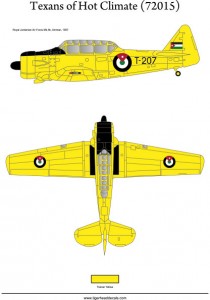
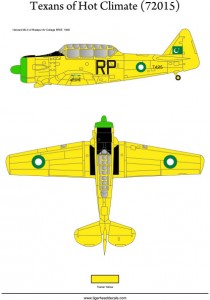
Texans of Hot Climate (72015)
T-6 “Texan”s are one of the most widely used trainers in the history of aviation. Its design was based on BC-1 basic trainer and the first order was received in 1937. In between 1938-1945 15,495 T-6 were produced. 10,057 of these planes were procured by the USAAC/USAAF and the remainder were deployed at the USN with the “SNJ” code and at 30 ally countries. The RAF was very interested in T-6s and they demanded great numbers. They were also produced under licence in Canada by Noorduyn.Those produced for the RAF and under licence in Canada were named “Harvard”s. Many USAAF pilots flew the T-6s before graduation and the pilots who participated the Battle of Britain and flew the Spitfires and the Hurricanes were trained on the British version “Harvard”s.
It is possible to make 6 full profiles.
– Pakistani Air Force 1948
– Royal Jordanian Air Force 1957
– Hellenic Air Force 1962
– Yemeni Air Force 1957
– Royal Egyptian Air Force 1949
– Turkish Air Force 1958.





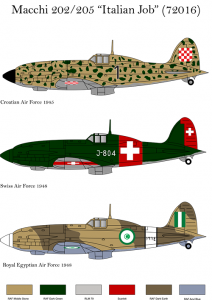
“Italian Job” Macchi 202/205 in International Service (72016)
The Macchi C.202 Folgore (Italian “thunderbolt”) was a World War II fighter aircraft built by Macchi Aeronautica and operated mainly by the Regia Aeronautica (RA; Royal (Italian) Air Force). Macchi aircraft designed by Mario Castoldi received the “C” letter in their model designation, hence the Folgore is referred to as the C.202 or MC.202. The C.202 was a development of the earlier C.200 Saetta, with an Italian built version of the Daimler-Benz DB 601Aa engine and with a redesigned, more streamlined fuselage. Considered to be one of the best wartime fighters to serve in large numbers with the Regia Aeronautica, the Folgore operated on all fronts in which Italy was involved.
It is possible to make 3 full profiles.
– Croatian Air Force 1945
– Swiss Air force 1948
– Royal Egyptian Air Force 1948.

Shooting Stars Around the World (72017)
The Lockheed T-33 Shooting Star (or T-Bird) is an American jet trainer aircraft. It was produced by Lockheed and made its first flight in 1948 piloted by Tony LeVier. The T-33 was developed from the Lockheed P-80/F-80 starting as TP-80C/TF-80C in development, then designated T-33A. It was used by the U.S. Navy initially as TO-2 then TV-2, and after 1962, T-33B. Despite its age, the T-33 remains in service worldwide.
It is possible to make 5 full profiles.
– Cuban Air Force
– Hellenic Air Force
– Italian Air Force
– Paraguay Air Force
– Turkish Air Force.






Spitfires in Russian Service (72018)
Along with British Hurricanes, the Soviet Air Force (voyenno-vozdushnyye sily—VVS) also managed to fly another aircraft of the Royal Air Force as a front-line fighter—the Spitfire Mk. Vb. In the West this airplane is feted as the winner of the Battle of Britain, and is also a national symbol of World War II. In the skies of Russia these fighters became participants in 1943 of the bloodiest battles over the Kuban. Two front-line fighter aviation regiments of the Soviet VVS—57th Guards Fighter Aviation Regiment (GIAP) and 821st Fighter Aviation Regiment (IAP)—were re-equipped with the Spitfire Mk. Vb.
It was the 57th GIAP that first entered combat with the enemy in these fighters, in May 1943. Earlier the regiment was known as the 36th IAP, and was formed in Baku in 1938. Pilots flew the regiment’s first combat sortie under the command of Major Aleksandr Alekseevich Osipov on 27 November 1941 as part of the 72d Fighter Aviation Division (IAD) (later the regiment was subordinated to the 237th IAD). The regiment fought in the Southern, Crimean, and North Caucasus fronts until 15 November 1942.
It is possible to make 3 full profiles.
– Spitfire Mk.Vb 57 GIAP Kuban 1943
– Spitfire Mk.IXe 26 GIAP Leningrad 1944-1945
– Spitfire Mk.IXc MJ858.


Spitfire MK.IXe in International Service (72019)
It is possible to make 3 full profiles.
– Turkish Air Force 1945
– Royal Norwegian Air force 1946
– Royal Egyptian Air Force 1948.


Spitfires All Around the World (72020)
It is possible to make 3 full profiles. It is suitable for 1/48 Eduard, Hasegawa and Italeri Spitfire Mk.Vc kits.
– Danish Air Force 1946
– Turkish Air Force 1948
– Hellenic Air Force 1946.

Hurricanes Around the World (72021)
It is possible to make 3 full profiles. It is suitable for 1/72 Airfix kit.
– Turkish Air Force
– Finnish Air Force
– Rumenian Air Force.

Hawker Sea Fury Part 2(72022)

Turkish Huns F100 C/D/F in TUAF Service(72023)

Spitfire Mk.Ixe in Turkish Service (72024)
After the WWII, the TuAF was inclined to make the “Spitfire”s her standart interceptor-fighter. An aggreement was signed with the Britsih firm Vickers for the overhaul and maintenance of the “Spitfire”s. In between Jan.1947 and Feb.1948 170 pcs Mk.IX were received. These planes were deployed at the 1st, 2nd, 3rd Co.s of the 4th Regiment, 3rd & 4th Co.s of the 5th Regiment 1st, 2nd, 3rd & 4th Co.s of the 7th Regiment and 1st, 2nd, 3rd & 4th Co.s of the 8th Regiment. Some of the planes were then transferred to the 1st, 2nd, 3rd & 4th Co.s of the 6th Regiment in 1949. After the reorganization of the TuAF they were deployed at the 4th & 6th Air Bases in 1951. They were written off in 1954. The Mk.IXs were equipped with a Rolls Royce Merlin 61 with an output of 1475HP. Their armament varied (some were equipped with 8 pcs 0.303 Caliper MGs whereas some were equipped with 4 pcs 0.303 caliper MG plus 2 pcs 20mm cannons. Some even had 4 pcs 20mm cannons and they were capable of carrying a bombload of 500lbs.

Exotic Starfighters(F-104 in TUAF, Pak and Jordanian)(72025)

Turkish Air Forces P-40E and P-40B(48001)
This decal set corresponds to the markings on the P-40B and P-40E aircrafts that served in the Turkish Air Force in the period of 1942-1948. The set allows you to complete 3 full profiles. This top quality decal set is printed by the company Microscale.
It is possible to make 2 full profiles of the E model with 6 different number alternatives. The guidebook enclosed to the sticker set demonstrates in details painting patterns and marking emplacements.






Turkish Air Forces TF-104 G (48002) Tigermeeters
Turkey is one of the very first countries to receive the F-104Gs within the MAP program. As a preparation for the new aircraft the 144th Squadron was organised at the 4th AB in Mürted-Ankara. The first 15 aircraft arrived on May 10th,1963 by sea and they were deployed at the newly founded squadron in July. In July 1963 two TF-104gs arrived and they were also assigned to the same squadron. This was followed by Canadair produced 18 F-104Gs and 2 TF-104Gs. The shipment continued in 1965 with 5 more Canadair built F-104Gs. All of these planes were deployed at the 144th Squadron. In 1968 3 pcs F-104G and 1 pc TF-104G were received from USAF.
The TuAF faced with the US embargo after the Cyprus peace-keeping Operation ordered a batch of 18 F-104S from Italy. 6 of the planes were delivered within the same year and the remainder in 1975 on the basis of the planes per month. In 1975 the purchase was risen to 40 planes all which were received within 1976.
The CF-104s, F-104Gs, TF-104Gs and the RF-104Gs which were strated being replaced by more modern aircraft were despatched to Turkey. This operation included 17 pcs F-104Gs from Belgium, 43 pcs F-104Gs & 12 pcs TF-104Gs from Holland, 12 pcs RF-104G and one TF-104G from Norway and 165 pcs F-104Gs and 36 pcs TF-104Gs from Germany. Canada also promised to hand over the CF-104s after being replaced by the F-18A/Bs. In 1986 44 pcs CF-104G & 6 pcs CF-104D were received. These planes were allocated to the 181st and to the 182nd Squadrons.

Turkish Air Forces Marking and Numbers Set (48003&48004)
TigerHead Decals is releasing a new Turkish Air Force marking and numbers set. This set that has been prepared for 1/48 and 1/72 scaled models also comprises tail numbers for F-104 and RF/F-4 series.


Turkish Air Forces P-47D Thunderbolt Stars and Crescent with Nose Arts(48005)
Among the most famous aircrafts of World War Two, P-47D Thunderbolts were used in the Turkish Air Force in the period of 1947-1954. Used at first in the 9th, 5th and 8th air regiments, the total number of aircrafts that came was 180.
Our decal set is made for use on models scaled 72 and 48 and comprises decals to complete a total of three aircraft models.


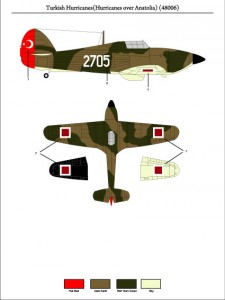
Turkish Hurricane (Hurricanes over Anatolia)(48006)
Hurricanes have started being used in the Turkish Air Force starting from 1939. During this period, a total of 164 of these aircrafts including the Mk.I, Mk.IIb and Mk.IIc/R models were put in service.They were taken out of the inventory of the Air Force in 1947 with the entry in service of the P-47D Thunderbolts. Our sticker set allows you to make two Mk.I (2710 and 2705), one Mk.IIb(2225) and one Mk.IIc (HV608).




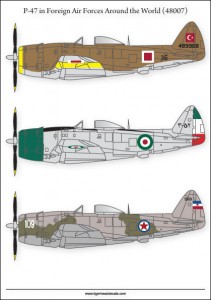
P-47 in Foreign Air Forces Around the World (48007)
Among the most famous aircrafts of World War Two, P-47D Thunderbolts were used in the Turkish, Iranian and Yugoslav Air Forces in the period of 1945-1962.
Our decal set is made for use on models scaled 48 and comprises decals to complete a total of three aircraft models.


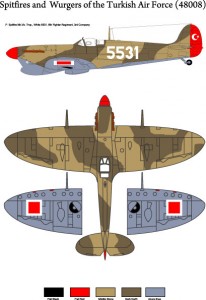
Spitfires and Wurgers of the Turkish Air Force (48008)
The procurement of the FW-190 A3s is the last link of a chain of Turco-German relations covering cooperation in aviation which started even before the WWI by the arrival of German planes and aviators at the Ottoman Empire. It was followed by the foundation of TOMTAŞ with the cooperation of Junkers in Kayseri which produced the Junkers A20s. In accordance with the agreements that were signed in the following years various German planes were procured and they served within the Turkish Armed Forces among which Rohrbach, Gotha and the earlier Focke Wolf models may be named. Another commercial agreement in between the two goverments was signed in 1941 after the great efforts of the German ambassador, former premier, Franz von Pappen. Turkey was to supply iron and chromium ores which were very strategic material for Germany and in return Turkey was to receive FW-190 A3s. 72 pcs FW-190 A3 arrived Turkey and the first flight was made on July.10th 1943. The planes were deployed at the 1st, 2nd, 3rd & 4th Co’s of the 5th Air Regiment. They were very much liked by the pilots and the crew and they remained in service until the end of 1947.
The Spitfires designed and produced by the British firm Vickers Supermarine participated the Battle of Britain and most probably they are the most popular fighters of WWII. Different models arrived Turkey at different times. A batch of 15 Spitfire MK.1s were ordered together with the Hawker “Hurricanes” but only 3 of them were delivered. One of them which was an ex-Polish order arrived in Sept.1938. The other two arrived in 1940. Eventhough serials 4501 to 4515 were allocated by the TuAF they were never used. The planes were deployed at the 42nd Hunter Company. Two of them were returned to RAFME in 1942. The Mk.1s were equipped with a Rolls Royce Merlin-2 engine with an output of 1030HP. Their armament consisted of 8 pieces 0.303 caliper MGs. They were distinctive with their 3-blade propeller.
No other Spitfire was supplied until mid-1944. In July 1944 39 pcs Mk.Vb was sent from RAF stocks. This was followed by 71 pcs Mk.Vc’s and 3 recce version Mk.V/R came in February 1945. Mk.Vb’s were deployed at the 1st and 2nd Co.s of the 5th Regiment, 1st, 2nd and 3rd Co.s of the 6th Regiment. The Mk.V/Rs were used with the “High Altitude Photo-Recce Unit”. These models were distinguished with their four-blade propellers. According to the TuAF sources they were equipped with Rolls Royce Merlin-20 engines with an output of 1500 HP. But the British sources state that the Mk.Vb’s were equipped with a 1585HP Rolls Royce Merlin 45M engine and the Mk.Vc’s with a 1470HP Rolls Royce Merlin 45 engine. The standart armament of the Mk.Vb’s were 4 pcs 0.303 caliper MG and 2 pcs 20mm cannon whereas the Mk.Vc’s had 4 pcs 20mm cannons and they were capable of carrying a bombload of 500lbs. They were replaced by the P-47 “Thunderbolts” in 1948.
After the WWII, the TuAF was inclined to make the “Spitfire”s her standart interceptor-fighter. An aggreement was signed with the Britsih firm Vickers for the overhaul and maintenance of the “Spitfire”s. In between Jan.1947 and Feb.1948 170 pcs Mk.IX were received. These planes were deployed at the 1st, 2nd, 3rd Co.s of the 4th Regiment, 3rd & 4th Co.s of the 5th Regiment 1st, 2nd, 3rd & 4th Co.s of the 7th Regiment and 1st, 2nd, 3rd & 4th Co.s of the 8th Regiment. Some of the planes were then transferred to the 1st, 2nd, 3rd & 4th Co.s of the 6th Regiment in 1949. After the reorganization of the TuAF they were deployed at the 4th & 6th Air Bases in 1951. They were written off in 1954. The Mk.IXs were equipped with a Rolls Royce Merlin 61 with an output of 1475HP. Their armament varied (some were equipped with 8 pcs 0.303 Caliper MGs whereas some were equipped with 4 pcs 0.303 caliper MG plus 2 pcs 20mm cannons. Some even had 4 pcs 20mm cannons and they were capable of carrying a bombload of 500lbs.
Only one Spitfire M.XI arrived. The exact date of arrival and deployment is not known. It was assigned to “High Altitude Photo-Recce Unit”. 4 pcs Mk.XIX were sold to Vickers by the RAF to make the overhaul. These planes were brought to Turkey in March 1947 and they were also deployed at the “High Altitude Photo-Recce Unit”. These planes were equipped 2 cameras underneath the fuselage an done each on the port and starboard sides of the fuselage. They were the most powerful Spitfires equipped with a 2035HP Rolls Royce Griffon engine. They are distinctive with their five-blade propeller. (From the www.tayyareci.com)





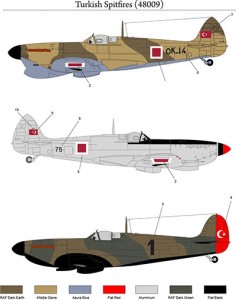
Turkish Spitfires (48009)
The Spitfires designed and produced by the British firm Vickers Supermarine participated the Battle of Britain and most probably they are the most popular fighters of WWII. Different models arrived Turkey at different times. A batch of 15 Spitfire MK.1s were ordered together with the Hawker “Hurricanes” but only 3 of them were delivered. One of them which was an ex-Polish order arrived in Sept.1938. The other two arrived in 1940. Eventhough serials 4501 to 4515 were allocated by the TuAF they were never used. The planes were deployed at the 42nd Hunter Company. Two of them were returned to RAFME in 1942. The Mk.1s were equipped with a Rolls Royce Merlin-2 engine with an output of 1030HP. Their armament consisted of 8 pieces 0.303 caliper MGs. They were distinctive with their 3-blade propeller.
No other Spitfire was supplied until mid-1944. In July 1944 39 pcs Mk.Vb was sent from RAF stocks. This was followed by 71 pcs Mk.Vc’s and 3 recce version Mk.V/R came in February 1945. Mk.Vb’s were deployed at the 1st and 2nd Co.s of the 5th Regiment, 1st, 2nd and 3rd Co.s of the 6th Regiment. The Mk.V/Rs were used with the “High Altitude Photo-Recce Unit”. These models were distinguished with their four-blade propellers. According to the TuAF sources they were equipped with Rolls Royce Merlin-20 engines with an output of 1500 HP. But the British sources state that the Mk.Vb’s were equipped with a 1585HP Rolls Royce Merlin 45M engine and the Mk.Vc’s with a 1470HP Rolls Royce Merlin 45 engine. The standart armament of the Mk.Vb’s were 4 pcs 0.303 caliper MG and 2 pcs 20mm cannon whereas the Mk.Vc’s had 4 pcs 20mm cannons and they were capable of carrying a bombload of 500lbs. They were replaced by the P-47 “Thunderbolts” in 1948.
After the WWII, the TuAF was inclined to make the “Spitfire”s her standart interceptor-fighter. An aggreement was signed with the Britsih firm Vickers for the overhaul and maintenance of the “Spitfire”s. In between Jan.1947 and Feb.1948 170 pcs Mk.IX were received. These planes were deployed at the 1st, 2nd, 3rd Co.s of the 4th Regiment, 3rd & 4th Co.s of the 5th Regiment 1st, 2nd, 3rd & 4th Co.s of the 7th Regiment and 1st, 2nd, 3rd & 4th Co.s of the 8th Regiment. Some of the planes were then transferred to the 1st, 2nd, 3rd & 4th Co.s of the 6th Regiment in 1949. After the reorganization of the TuAF they were deployed at the 4th & 6th Air Bases in 1951. They were written off in 1954. The Mk.IXs were equipped with a Rolls Royce Merlin 61 with an output of 1475HP. Their armament varied (some were equipped with 8 pcs 0.303 Caliper MGs whereas some were equipped with 4 pcs 0.303 caliper MG plus 2 pcs 20mm cannons. Some even had 4 pcs 20mm cannons and they were capable of carrying a bombload of 500lbs.
Only one Spitfire M.XI arrived. The exact date of arrival and deployment is not known. It was assigned to “High Altitude Photo-Recce Unit”. 4 pcs Mk.XIX were sold to Vickers by the RAF to make the overhaul. These planes were brought to Turkey in March 1947 and they were also deployed at the “High Altitude Photo-Recce Unit”. These planes were equipped 2 cameras underneath the fuselage an done each on the port and starboard sides of the fuselage. They were the most powerful Spitfires equipped with a 2035HP Rolls Royce Griffon engine. They are distinctive with their five-blade propeller. (From the www.tayyareci.com)


Early Arabic Mig-21 F13 Fishbeds(48010)
The Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-21 (Russian: Микоян и Гуревич МиГ-21; NATO reporting name: Fishbed) is a supersonic jet fighter aircraft, designed by the Mikoyan-Gurevich Design Bureau in the Soviet Union. It was popularly nicknamed “Balalaika”, from the aircraft’s planform-view resemblance to the Russian stringed musical instrument or ołówek (English: pencil) by Polish pilots due to the shape of its fuselage.
Early versions are considered second-generation jet fighters, while later versions are considered to be third-generation jet fighters. Some 50 countries over four continents have flown the MiG-21, and it still serves many nations a half-century after its maiden flight. The fighter made aviation records. At least by name, it is the most-produced supersonic jet aircraft in aviation history and the most-produced combat aircraft since the Korean War, and it had the longest production run of a combat aircraft (1959 to 1985 over all variants)





Turkish Air Forces F-104 G (48011) Tigermeeters
Turkey is one of the very first countries to receive the F-104Gs within the MAP program. As a preparation for the new aircraft the 144th Squadron was organised at the 4th AB in Mürted-Ankara. The first 15 aircraft arrived on May 10th,1963 by sea and they were deployed at the newly founded squadron in July. In July 1963 two TF-104gs arrived and they were also assigned to the same squadron. This was followed by Canadair produced 18 F-104Gs and 2 TF-104Gs. The shipment continued in 1965 with 5 more Canadair built F-104Gs. All of these planes were deployed at the 144th Squadron. In 1968 3 pcs F-104G and 1 pc TF-104G were received from USAF.
The TuAF faced with the US embargo after the Cyprus peace-keeping Operation ordered a batch of 18 F-104S from Italy. 6 of the planes were delivered within the same year and the remainder in 1975 on the basis of the planes per month. In 1975 the purchase was risen to 40 planes all which were received within 1976.
The CF-104s, F-104Gs, TF-104Gs and the RF-104Gs which were strated being replaced by more modern aircraft were despatched to Turkey. This operation included 17 pcs F-104Gs from Belgium, 43 pcs F-104Gs & 12 pcs TF-104Gs from Holland, 12 pcs RF-104G and one TF-104G from Norway and 165 pcs F-104Gs and 36 pcs TF-104Gs from Germany. Canada also promised to hand over the CF-104s after being replaced by the F-18A/Bs. In 1986 44 pcs CF-104G & 6 pcs CF-104D were received. These planes were allocated to the 181st and to the 182nd Squadrons.

Early Mig-21 Fishbeds Volume 2 (48013)
The Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-21 (Russian: Микоян и Гуревич МиГ-21; NATO reporting name: Fishbed) is a supersonic jet fighter aircraft, designed by the Mikoyan-Gurevich Design Bureau in the Soviet Union. It was popularly nicknamed “Balalaika”, from the aircraft’s planform-view resemblance to the Russian stringed musical instrument or ołówek (English: pencil) by Polish pilots due to the shape of its fuselage.
Early versions are considered second-generation jet fighters, while later versions are considered to be third-generation jet fighters. Some 50 countries over four continents have flown the MiG-21, and it still serves many nations a half-century after its maiden flight. The fighter made aviation records. At least by name, it is the most-produced supersonic jet aircraft in aviation history and the most-produced combat aircraft since the Korean War, and it had the longest production run of a combat aircraft (1959 to 1985 over all variants)






Mediterranean C-47’s (48014)
110 C-47A/Bs and DC-3s served the Turkish Armed Forces and the Turkish Air Force. But it was the Turkish State Airlines who was the first to buy 30 C-47s from the RAFME stocks in Cairo in 1945 in order to renew the fleet and to expand the existing routes. This was followed by the procurement of 18 C-47As with the sources allocated from the national budget in 1946. They joined The Turkish Armed Forces in 1948. It was soon followed by 81 C-47A/Bs supplied from the USAF stocks in Germany within the American Military Aid Programme, The shipment started in August 13, 1948 and it was completed in April 24, 1949. But 7 of these planes which arrived in 1949 were then delivered to an unknown destination most probably to Persia within the same year(1). The last C-47s added to the inventory were 11 planes 2 of which were acquired from Libya, one from the Turkish Airport Authorithies (DHMI) and one from the Turkish Mineral Exploration Agency (MTA) one from USAFE and 6 from THY (Turkish Airlines) which were used as VIP transports. The planes which were acquired from USAFE and THY were given the Turkish Military Serials which were previously assigned to those 7 planes delivered to an unknown destination(1).
C-47s served in the TuAF for a long period of time and they often worked side by side with C-130s and with C-160s. They flew the “Western Courier” and the “Eastern Courier” routines starting from the Etimesgut Military Airport. They were started to be replaced by the CASA CN-235s in Dec. 1993. Three EC-47s which were converted into ECM planes remained in service until 1995. The last C-47 was replaced in 1998.


Hawker Sea Fury (48015)
The Hawker Sea Fury was a British fighter aircraft designed and manufactured by Hawker. It was the last propeller-driven fighter to serve with the Royal Navy, and also one of the fastest production single piston-engined aircraft ever built. Developed during the Second World War, the Sea Fury entered service two years after the war ended. The Sea Fury proved to be a popular aircraft with a number of overseas militaries, and was used during the Korean War in the early 1950s.
The Sea Fury’s development was formally initiated in 1943 in response to a wartime requirement of the RAF, thus the aircraft was initially named Fury. As the Second World War drew to a close, the RAF cancelled their order for the aircraft; however, the Royal Navy saw the type as a suitable carrier aircraft to replace a range of increasingly obsolete or poorly suited aircraft being operated by the Fleet Air Arm. Development of the Sea Fury proceeded, and the type began entering operational service in 1947.



Shooting Stars Around the World (48016)
The Lockheed T-33 Shooting Star (or T-Bird) is an American jet trainer aircraft. It was produced by Lockheed and made its first flight in 1948 piloted by Tony LeVier. The T-33 was developed from the Lockheed P-80/F-80 starting as TP-80C/TF-80C in development, then designated T-33A. It was used by the U.S. Navy initially as TO-2 then TV-2, and after 1962, T-33B. Despite its age, the T-33 remains in service worldwide.
It is possible to make 6 full profiles.
– Cuban Air Force
– Hellenic Air Force
– Italian Air Force
– Paraguay Air Force
– Turkish Air Force






Hellenic Spitfires (48017)
The 336th Sqdn “Olympus” received the first Spitfire. The receival of new Spits took place at Araxos AB on 14-11-1944. In the end of 1945 RHAF stopped being depended on RAF and the Mk.Vb/c were given to Greece on 25/4/1946. In January 1947 were delivered the Spitfires Mk.IX. On the February of 1949, were delivered the new Spitfires Mk.XVIe.



“Italian Job” Macchi 202/205 in International Service (48018)
The Macchi C.202 Folgore (Italian “thunderbolt”) was a World War II fighter aircraft built by Macchi Aeronautica and operated mainly by the Regia Aeronautica (RA; Royal (Italian) Air Force). Macchi aircraft designed by Mario Castoldi received the “C” letter in their model designation, hence the Folgore is referred to as the C.202 or MC.202. The C.202 was a development of the earlier C.200 Saetta, with an Italian built version of the Daimler-Benz DB 601Aa engine and with a redesigned, more streamlined fuselage. Considered to be one of the best wartime fighters to serve in large numbers with the Regia Aeronautica, the Folgore operated on all fronts in which Italy was involved.
It is possible to make 3 full profiles.
– Croatian Air Force 1945
– Swiss Air force 1948
– Royal Egyptian Air Force 1948.


Spitfires in Russian Service (48019)
Along with British Hurricanes, the Soviet Air Force (voyenno-vozdushnyye sily—VVS) also managed to fly another aircraft of the Royal Air Force as a front-line fighter—the Spitfire Mk. Vb. In the West this airplane is feted as the winner of the Battle of Britain, and is also a national symbol of World War II. In the skies of Russia these fighters became participants in 1943 of the bloodiest battles over the Kuban. Two front-line fighter aviation regiments of the Soviet VVS—57th Guards Fighter Aviation Regiment (GIAP) and 821st Fighter Aviation Regiment (IAP)—were re-equipped with the Spitfire Mk. Vb.
It was the 57th GIAP that first entered combat with the enemy in these fighters, in May 1943. Earlier the regiment was known as the 36th IAP, and was formed in Baku in 1938. Pilots flew the regiment’s first combat sortie under the command of Major Aleksandr Alekseevich Osipov on 27 November 1941 as part of the 72d Fighter Aviation Division (IAD) (later the regiment was subordinated to the 237th IAD). The regiment fought in the Southern, Crimean, and North Caucasus fronts until 15 November 1942.
It is possible to make 3 full profiles.
– Spitfire Mk.Vb 57 GIAP Kuban 1943
– Spitfire Mk.IXe 26 GIAP Leningrad 1944-1945
– Spitfire Mk.IXc MJ858.


Sukhoi Su-2 (48020)
The Sukhoi Su-2 (Russian: Сухой Су-2) was a Soviet scout and light bomber aircraft used in the early stages of World War II. It was the first airplane designed by Pavel Sukhoi. The basic design received an engine and armament upgrade (Su-4) and was modified for the ground attack role (ShB).
It is possible to make 4 full profiles. It is suitable for 1/48 Zvezda kit.
– Stalingrad Front August 1942
– Stalingrad Front August 1942 52nd BAP
– Moscow Front January 1942
– Unidentified Unit 1941.


Spitfire MK.IXe in International Service (48021)
Structurally unchanged from the C wing. The outer machine gun ports were eliminated, although the outer machine gun bays were retained and their access doors were devoid of empty shell case ports and shell deflectors. The inner gun bays allowed for two weapon fits;
2 × 20 mm Hispano Mk II cannon with 120 rpg in the outer bays.
2 × .50 cal Browning M2 machine guns, with 250 rpg in the inner bays.
or 4 × 20 mm Hispano cannon with 120 rpg
The .303 machine guns mounted in the outer wings were no longer fitted as most aircraft at that time had armour impenetrable by .303 bullets. During a turning combat the effectiveness of the outboard machine guns was low because if the aircraft was pulling ‘g’ the flexing of the wings meant that the rounds scattered in a large cone. The 20 mm Hispano cannon were moved outboard and a more effective .50 calibre Browning .50 cal M2/AN heavy machine gun with 250 rpg was added to the inner gun-bay. The first trial installation of the installation (modification 1029) was made in BS118 in November 1943; by mid-March 1944 the first Spitfires to be modified were from 485(NZ), 222 and 349 Squadrons. Spitfires with this armament were referred to as Spifire IX LF .5 and the E suffix was not officially introduced until early 1945. This armament was standard for all Spitfire Mk IXs and XVIs used by the 2nd Tactical Air Force as fighters and fighter-bombers from shortly after D-Day. The improved armament was more effective for both air-to-air engagements and air-to-ground attacks.[9]
Many Spitfires had their rounded wingtips replaced by shorter, squared off fairings to improve low-altitude performance and enhance the roll rate. These are sometimes referred to as “LF” versions, e.g. LF.IX. This designation referred to the low-altitude version of the Rolls-Royce Merlin engine, and, while many “LF” Spitfires had the “clipped” wings, a number did not.
It is possible to make 3 full profiles.
– Turkish Air Force 1945
– Royal Norwegian Air force 1946
– Royal Egyptian Air Force 1948.


Exotic Spitfires (48022)
The Rolls-Royce Griffon engine was designed in answer to Royal Naval specifications for an engine capable of generating good power at low altitudes. The concepts for adapting the Spitfire to take the new engine had begun as far back as October 1939; Joseph Smith felt that “The good big ‘un will eventually beat the good little ‘un.” and Ernest Hives of Rolls-Royce thought that the Griffon would be “a second power string for the Spitfire.”[1] The first of the Griffon-engined Spitfires flew on 27 November 1941.
Although the Griffon-engined Spitfires were never produced in the large numbers of the Merlin-engined variants they were an important part of the Spitfire family and, in their later versions, kept the Spitfire at the forefront of piston-engined fighter development.
It is possible to make 4 full profiles.
– Royal Air Force
– Southern Rhodesia Air Force
– Egyptian Air Force
– Syrian Air Force.


Spitfires All Around the World (48023)
It is possible to make 3 full profiles. It is suitable for 1/48 Eduard, Hasegawa and Italeri Spitfire Mk.Vc kits.
– Danish Air Force 1946
– Turkish Air Force 1948
– Hellenic Air Force 1946.

Texans of Hot Climate (48024)
T-6 “Texan”s are one of the most widely used trainers in the history of aviation. Its design was based on BC-1 basic trainer and the first order was received in 1937. In between 1938-1945 15,495 T-6 were produced. 10,057 of these planes were procured by the USAAC/USAAF and the remainder were deployed at the USN with the “SNJ” code and at 30 ally countries. The RAF was very interested in T-6s and they demanded great numbers. They were also produced under licence in Canada by Noorduyn.Those produced for the RAF and under licence in Canada were named “Harvard”s. Many USAAF pilots flew the T-6s before graduation and the pilots who participated the Battle of Britain and flew the Spitfires and the Hurricanes were trained on the British version “Harvard”s.
It is possible to make 5 full profiles.
– Pakistani Air Force 1948
– Royal Jordanian Air Force 1957
– Hellenic Air Force 1962
– Royal Egyptian Air Force 1949
– Turkish Air Force 1958.







Spitfire Mk.IXe in Turkish Service (48025)
After the WWII, the TuAF was inclined to make the “Spitfire”s her standart interceptor-fighter. An aggreement was signed with the Britsih firm Vickers for the overhaul and maintenance of the “Spitfire”s. In between Jan.1947 and Feb.1948 170 pcs Mk.IX were received. These planes were deployed at the 1st, 2nd, 3rd Co.s of the 4th Regiment, 3rd & 4th Co.s of the 5th Regiment 1st, 2nd, 3rd & 4th Co.s of the 7th Regiment and 1st, 2nd, 3rd & 4th Co.s of the 8th Regiment. Some of the planes were then transferred to the 1st, 2nd, 3rd & 4th Co.s of the 6th Regiment in 1949. After the reorganization of the TuAF they were deployed at the 4th & 6th Air Bases in 1951. They were written off in 1954. The Mk.IXs were equipped with a Rolls Royce Merlin 61 with an output of 1475HP. Their armament varied (some were equipped with 8 pcs 0.303 Caliper MGs whereas some were equipped with 4 pcs 0.303 caliper MG plus 2 pcs 20mm cannons. Some even had 4 pcs 20mm cannons and they were capable of carrying a bombload of 500lbs.

Total 6 pieces.
(2x inlet plug, 2x exhaust plug, 1x gun cover, 1x gun scoop inlet cover









Son yorumlar